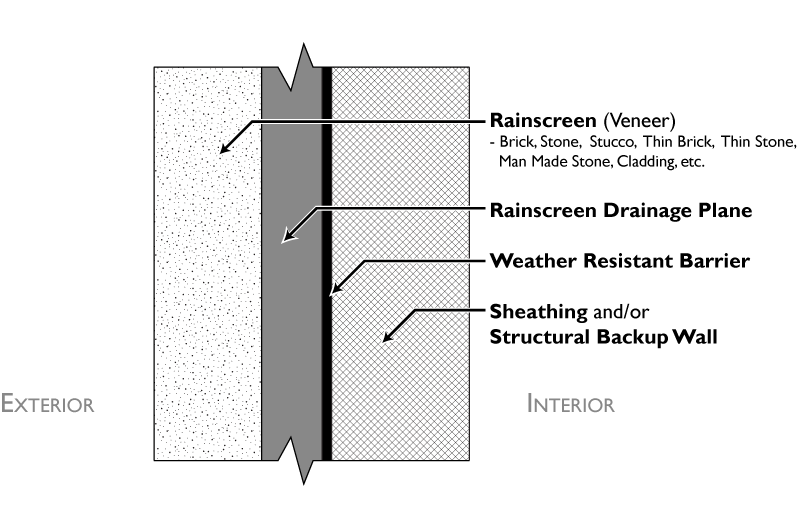
The main function of a rain screen is to protect external walls on a building from rains or any other climatic changes. They divert water direction and can save the walls of the building from moisture issues. All rain screens usually have external cladding as well.
Cladding basically refers to a process of covering a material with a different one. The surface of this material which gets covered is usually finished and cladding is an additional protective coating. The external walls or roof of all buildings should be sheltered by adding a layer for driving water away from the surface which requires protection.
 Rain screen cladding could be made out of wood, glass, stone, metal or masonry. It reduces the force of rain which strikes a protected surface. The cavity on the back will reduce the thrust with which rainwater flows over the support wall. Generally, it is porous in nature and even has vents inside which help facilitate air flow towards the cavity and prevents moisture from building up inside the cavity. Also airtight supporting walls, with covering of waterproof materials ensure moisture does not cause harm to the structure at all.
Rain screen cladding could be made out of wood, glass, stone, metal or masonry. It reduces the force of rain which strikes a protected surface. The cavity on the back will reduce the thrust with which rainwater flows over the support wall. Generally, it is porous in nature and even has vents inside which help facilitate air flow towards the cavity and prevents moisture from building up inside the cavity. Also airtight supporting walls, with covering of waterproof materials ensure moisture does not cause harm to the structure at all.
There are two basic types of rain screens:
- Simple rain screens
- Pressure-equalized rain screens
The first type is usually enough for handling low rainfall. This cladding is vented and is airtight. The base will also have a drain.
But balancing the two pressures doesn’t work so well in practice. That is why it helps if the cavity is compartmentalized. In order to further prevent any rainwater from breaking through the cladding, the joint sizes can help provide great results. In order to get best results, it is important for quality sealants to be employed and as well as drainage layers over support walls to make sure pressure balancing is working efficiently.
It’s quite essential for buildings to have rain screens. They help ensure the external walls are strong for a long period of time.